The decision to outsource various supply chain functions and processes to a Third Party Logistics (3PL) company can be challenging yet rewarding to an organization. Supply chain functions have grown increasingly complex with globalization, technology, and competition advancing at a rapid pace. Thoroughly examining the motivations, expectations, and justifications for outsourcing critical supply chain functionality enables companies to make effective decisions which generate incremental profitability and shareholder value. Careful consideration and analysis of cost factors, performance gaps, financial impact, and suitability for outsourcing yields superior outsourcing strategies and transition plans.
Outsourcing ultimately requires trust. Handing over various aspects of supply chain operations to a partner can be difficult for organizations that do not typically view their suppliers as cooperative partners. Entering a relationship with a 3PL company is like handing over your wallet to a business associate – do you trust that your cash, credit cards, and family photos will be intact when you ask for it back? With a 3PL contract – you issue goods to a carrier or receipts into a warehouse, you issue orders to ship or deliver to specific consignees, and you expect perfect execution and inventory balances.
In response to market demands for speed, accuracy, visibility, globalization, and electronic communications, many companies turn to outsourcing of supply chain operations including warehousing, transportation, materials planning, freight forwarding and reverse logistics. The general motivations for outsourcing these operations fall into three main categories: increase revenue, improve capabilities, and reduce cost. As illustrated in Figure 1, multiple motivations fall into each category.
Figure 1. General Outsourcing Motivations
|
Increase Revenue |
Improve Capabilities |
Reduce Cost |
| Increase supply chain flexibility & responsiveness | Focus on core business | Reduce operating costs |
| Increase speed to market | Gain access to new technology | Reduce capital investment |
| Improve quality | Gain access to advanced skills | Transform fixed to variable costs |
| Decrease customer response time | Provide flexible facility capacity | Meet downsizing requirements |
| Gain access to new markets | Create additional capacity | Reduce development costs |
| Provide backup capability | Reduce healthcare exposure |
While these valid and appropriate motivations drive outsourcing decisions, some companies use inappropriate reasons to justify their decision to outsource. Some companies choose to outsource simply due to lack of understanding of logistics processes. Lack of necessary skills may be a valid reason for outsourcing but companies should maintain enough knowledge of their logistics processes in order to effectively manage the outsourced relationship. Other companies justify their outsourcing decision on the ability to better identify the true cost of supply chain operations. Companies should first seek to understand their true logistics costs prior to outsourcing in order to make better decisions and build better relationships. Some companies want to off load the problems and issues associated with managing logistics operations. They mistakenly believe they can transfer the inherent problems and shift responsibility to a partner for resolution. The result of this belief will manifest itself in frustration, anger, blame, and poor logistics performance. Desire to simply reduce headcount is another inappropriate outsourcing motivation as is the desire to simply reduce the asset base in order to achieve a short term improvement in the eyes of public investors. Outsourcing motivations will ultimately impact partner relationships and supply chain performance either positively or negatively.
Some companies never consider outsourcing or eliminate the strategic option of outsourcing too early in the supply chain strategy development cycle due to reasons that can be just as inaccurate or inappropriate as poor reasons to outsource. In-sourcing rationale may include:
- An unconfirmed perception that cost will increase if an operation is outsourced. In many cases, this view is expressed by companies that do not know their true cost of supply chain operations.
- Belief that customer complaints will automatically increase due to decreases in overall service levels. The belief is that the partner will not care about the business as much as internal employees do which will not be the case if expectations are properly established and contracts properly structured.
- The perception that only company employees can know their business well enough to effectively serve their customers and no other company could ever do it as well. Their products and market offer may be truly unique but a qualified and experienced 3PL partner may have superior processes for order processing, storage, fulfillment, EDI, packing, labeling, and shipping which could actually better serve their customers.
- Fear of “losing control”. In reality, a well-structured 3PL agreement may yield increased control as 3PLs are operating under a customer centric, cost focused relationship in which all transactions are recorded, monitored and reported on a daily, weekly and monthly basis.
When pursuing a strategy of outsourcing, a company must objectively evaluate its operations relative to outsourcing options. An outsourcing evaluation team should include members from the supply chain organization, finance or accounting, and sales. The evaluation and decision should consider cost analysis, performance gap analysis, financial opportunities, and suitability of operations for outsourcing.
- Cost analysis should include all of the costs associated with operations, including those costs that will be transferred to a service partner and those that will remain with the company.
- Performance gap analysis should include an objective assessment of company performance, strengths, and weaknesses supported by metrics and benchmarking comparisons if necessary. Outside expertise can be very useful for performance gap analysis in order to obtain objective results.
- Financial opportunities assessment includes reviews of fixed to variable cost conversions, potential cost of technology upgrades, matching cost to volume fluctuations, and benefits to the balance sheet or corporate capital structure.
- Suitability analysis refers to objectively evaluating process details in light of the performance gaps to determine the most likely candidates for enhancement through outsourcing.
Cost analysis is critical prior to engaging in an outsourcing process for logistics or supply chain operations. The team must evaluate warehousing costs for space, labor, and technology relative to activity profiles. Detailed analysis of inbound and outbound transportation cost should be summarized by location and mode. The team must identify costs of customer service operations and inventory investment that can also be impacted by an outsourcing option.
Identifying and understanding all of the operational costs is important as an input for making the decision to outsource logistics operations. Recognizing regional differences and understanding the business, product, customer, or facility drivers that influence cost performance is important to developing functional requirements and evaluating future vendor proposals. Once all of the costs are identified and documented, the team should project which costs will be transferred to potential service providers and which will be retained after outsourcing. Some providers may propose different levels of service or optional services that can transfer or defer different cost components. Cost analysis is an important initial step of the total outsourcing analysis and justification process.
The logistics performance gap analysis is used to compare logistics key performance indicators with world-class indicators. The gap analysis enables assessment of strengths and weaknesses; identification of complementary logistics partners; and development of cost-benefit justification of a world-class logistics initiative. Many companies must collect and summarize their operational performance data in order to develop many key performance indicators if they are not currently 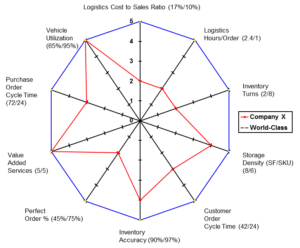
Once the gaps are identified, the team should use them to better understand the strengths and weaknesses of the organization. The gap analysis enables the company to seek partners with strengths that can compensate for or complement the weaknesses or capability gaps which the company should strive to fill. A decision to outsource operations will then yield an evaluation requirement to leverage the expertise of potential partners to fill the most significant gaps in performance capability. Remember, that filling the gaps will take some time even for highly qualified partners as the company must adapt and develop internal processes to capitalize on the improved capabilities.
The team must evaluate financial opportunities relative to current cost factors, capital investment requirements for closing performance gaps, financial structure and objectives, volume variability and company risk tolerance. The analysis should consider current unit costs and the mix of fixed and variable costs and potential to convert fixed to variable cost. If gaps exist in technology capability, the team should estimate the capital investment required to adequately fill the technology gap and the time required for implementation. If the volume fluctuates significantly, conversion to variable cost will enable the company to more closely match period costs to volume resulting in a more stable cost per unit per period. Elimination of facility leases or sales of distribution facilities or fleet operations can have positive balance sheet impacts which can contribute extra savings or benefits to the outsourcing justification.
World-class logistics organizations partner with strategic providers of various logistics services including transportation management, transportation services, freight forwarding, customs brokerage, warehousing, logistics information systems, benchmarking, logistics consulting, and logistics professional education. The outsourcing decision for any one of these logistics services must be reviewed periodically (as the business and logistics environment is changing perpetually) and carefully (since it is typically more difficult to re-insource an activity). Outsourcing decisions should consider the following decision criteria to justify outsourcing a logistics activity. Consider logistics outsourcing if:
- Proven 3PL providers support your industry or support businesses with similar operational attributes AND
- Economies of scope and scale are available for a 3PL AND
- 3PLs potentially have a significant cost and service advantage AND
- Outsourcing will fill operational performance gaps AND
- Outsourcing will not adversely impact customer communications and relationships AND
- The 3PLs have a better warehouse management system or can effectively operate using your existing WMS
Once the decision to outsource is made, the team will begin the implementation process by creating the outsourcing plan and preliminary budgets and schedules.
Remember to check out the first and second posts in this series regarding Outsourcing Motivations and Assessment.
Part Two: Logistics Outsourcing: Is it right for your business? Part 2 – Assessment and Cost Analysis
Part Three: Logistics Outsourcing: Is it right for your business? Part 3 – Assessment, Gap Analysis
As of September 8, 2020, Crimson & Co (formerly The Progress Group/TPG) has rebranded as Argon & Co following the successful merger with Argon Consulting in April 2018.







